Swanson CoQ10 100mg
6.495 kr.
- 100 Hylki (100 skt.)
- 100mg í hverju hylki
Ekki til á lager
Láta mig vita þegar vara kemur aftur
FÁÐU SENT EÐA SÆKTU | LÍTILL PAKKI
Frí sending ef þú pantar vörur í þessum flokk fyrir meira en 15.000 kr.
- Heimsending með TVG Xpress: 995 kr.
- Sent á pósthús: 795 kr.
- Sækja í verslun: Frítt
Coenzyme Q10 is an important molecule for cellular energy production – it aids the mitochondria, the energy producing organelles of the cells, to do their job efficiently and this in turn results in better cellular health. CoQ10 is known as a pseudo-vitamin because it does not necessarily need to be supplemented (the human organism can manufacture it) but it is as important for the human body as a vitamin and supplementation can lead to better management of a lot of medical conditions. Intake of CoQ10 can also improve the cellular energy status of healthy people so this molecule is suggested to be a staple of the supplementation regimen of most people. Other names for CoQ10 include Ubiquinol and Ubiquinone because these are forms the molecule can take in the human body but both of them are interchangeable and can be supplemented. Coenzyme Q10 is also contained in a number of foods – meat (beef, pork, chicken) has the highest concentrations; fish, dairy, eggs, and nuts are poorer sources; and plants are not good sources for this nutrient. The problem is that the best concentration of CoQ10 is in the heart muscle and liver of animals and since most people do not consume these animal organs regularly, taking a supplement is the more practical option.
A number of disease states are associated with low levels of CoQ10 – fibromyalgia, post-myocardial infarction, Prader-Willi syndrome, male infertility, Peyronie’s disease, migraines, and Parkinson’s disease; frequent smokers also show low CoQ10 levels. If one is diagnosed with any of these diseases supplementation of CoQ10 is recommended and that is so especially for victims of heart attack and fibromyalgia patients. Healthy people can also benefit from supplementation of CoQ10 as the molecule is known to improve blood flow and protect blood vessels from damage due to oxidized cholesterol molecules as well as reduce arterial plaque buildup.
Various supplementation amounts have been tested and doses ranging from 30 mg to 400-500 mg have been proven to be effective in increasing blood and tissue levels of Ubiquinol. The most commonly recommended dose is around 90-120 mg per day taken with a meal as food intake enhances absorption and storage. Since CoQ10 is a fat soluble nutrient it is best to take it with a meal containing dietary fat and most supplements use oil-based suspensions for CoQ10 delivery. There are, however, patented water-soluble versions that show similar bioavailability and efficacy as well as safety profile so it is a matter of preference which form a person chooses to use. Regarding safety CoQ10 is proven to show no adverse or side effects with doses up to 900 mg after long-term usage so intake of the recommended dosages should not be of any concern.
Multiple human studies have tested the effects of CoQ10 supplementation with important physiological and health-relevant results. Taking CoQ10 can decrease levels of oxidative stress in the body, decrease blood pressure, improve blood flow (especially in conditions characterized by increased oxidative stress and worsened blood flow), improve blood vessel state and function, increase anti-oxidant enzymes in the body, and generally improve quality of life (especially for diseased people). It is also beneficial to take CoQ10 with regular physical exercise – exercise-induced oxidation is decreased and there might be an anti-fatigue effect when supplementing this molecule; people with myocardial infarction can experience better exercise capacity; a reduced muscle damage due to exercise has also been recorded; exercising people experience a decrease in the rate of perceived exertion which means they can tolerate their sports regimens better. Multiple medical conditions can be improved with CoQ10 supplements – there are strong effects on reducing symptoms of fibromyalgia (chronic muscle pain, fatigue, sleep problems, and painful tender points or trigger points) and symptoms of Peyronie’s disease (a form of erectile dysfunction); some evidence exists for decreasing symptoms of Parkinson’s disease as well as migraine and headache symptoms and frequency; infertile men can also experience an increase in their testosterone levels and the overall quality of their sperm is improved by taking CoQ10. Overall, patients with various diseases and most healthy individuals can benefit from taking a CoQ10 supplement as only positive results and no side effects have been noted in clinical human investigations of this molecule.
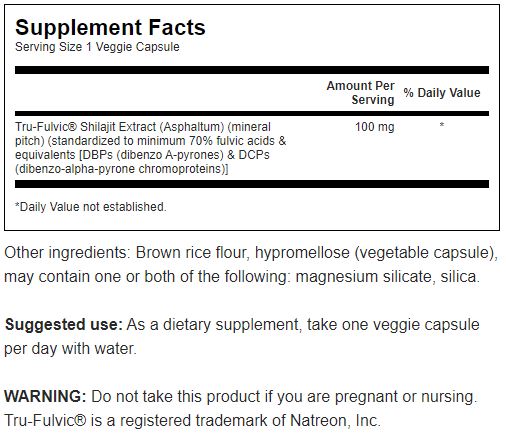
Innihaldslýsing
BCAA
3.799 kr. – 7.999 kr.Creatine Monohydrate
3.399 kr. – 6.599 kr.FlipBelt vatnsbrúsi
1.795 kr. – 1.995 kr.Batterí íþróttadrykkur
3.799 kr.PhD Diet Whey
3.195 kr. – 9.995 kr.PhD Smart Bar Próteinstangir
449 kr.SiS GO Isotonic orkugel
279 kr.Soy prótein Isolate
3.999 kr.OPNUNARTÍMI
- Virka daga: 10-18
- Laugardaga: 11-15
- Sunnudaga: Lokað
- Páskar (17-21 Apríl.): Lokað